
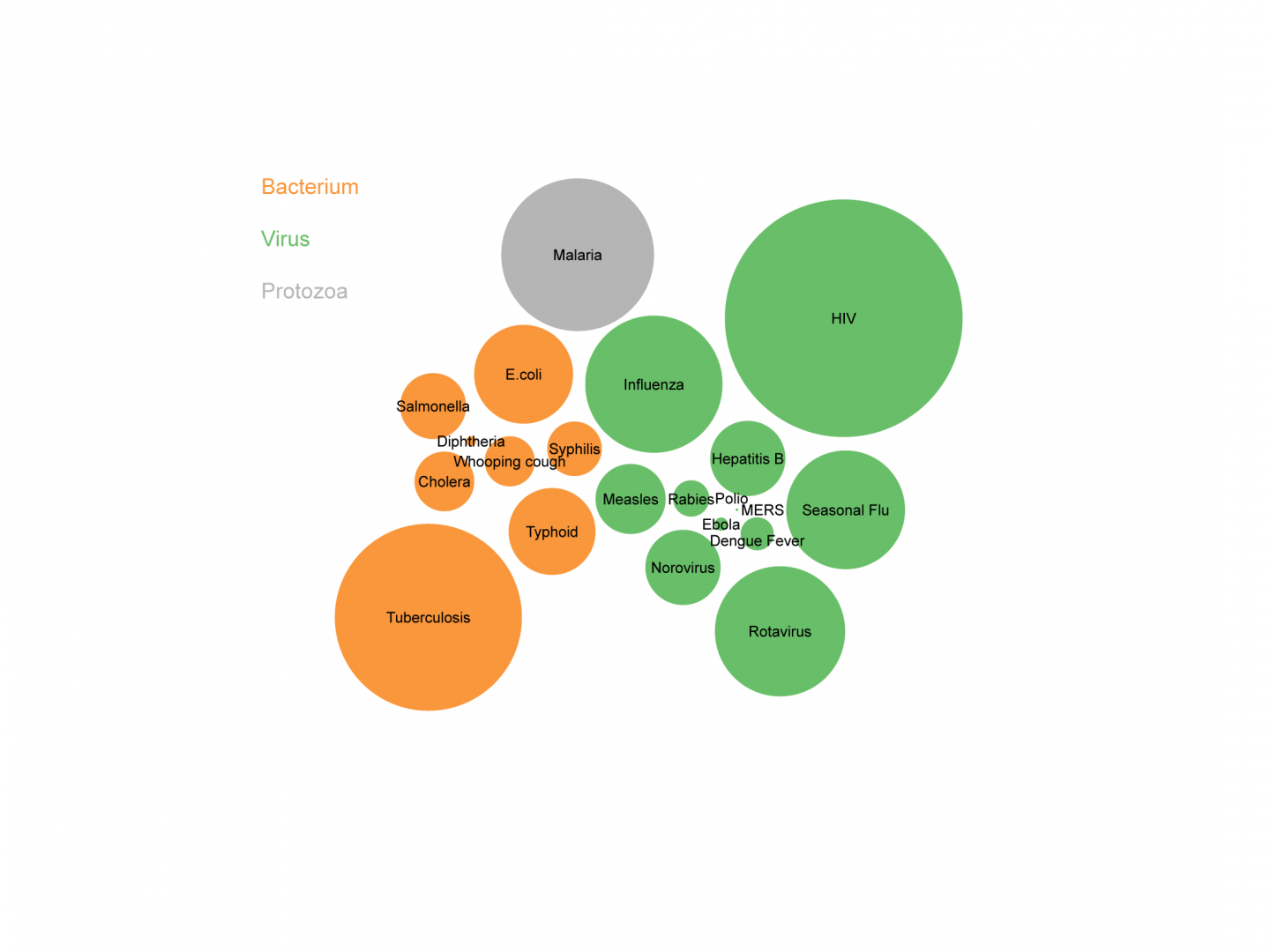
The plot of markers across the visualization helps you to categorize the data, based on your use case. The scatter plot and bubble chart are best used when comparing paired numerical data, not necessarily associated to a time dimension.
#Bubble chart how to
To learn how to add a scatter plot or bubble chart to a board or worksheet, see Configure a chart card.
Via this filter, users can navigate different branches of the list hierarchy in the source model. The hierarchy filter selector displays on the published chart, for that card on your board or worksheet. On the Context tab you can toggle hierarchy filters. Toggle right on Use conditional formatting from.
#Bubble chart series
After updating the chart, go to the Chart tab, and expand the Series section. To use conditional formatting in scatter plots and bubble charts, follow the process in Configure conditional formatting. In this case, formatting is defined by your source view's fourth column of data. This allows you to set statuses to color the bubble or plot markers based on rules and values. Scatter plots and bubble charts can also use conditional formatting. Due to their nature, Logarithmic trendlines cannot contain nonpositive (greater-than-zero) values in the Z-axis and will be unavailable if these values are present.
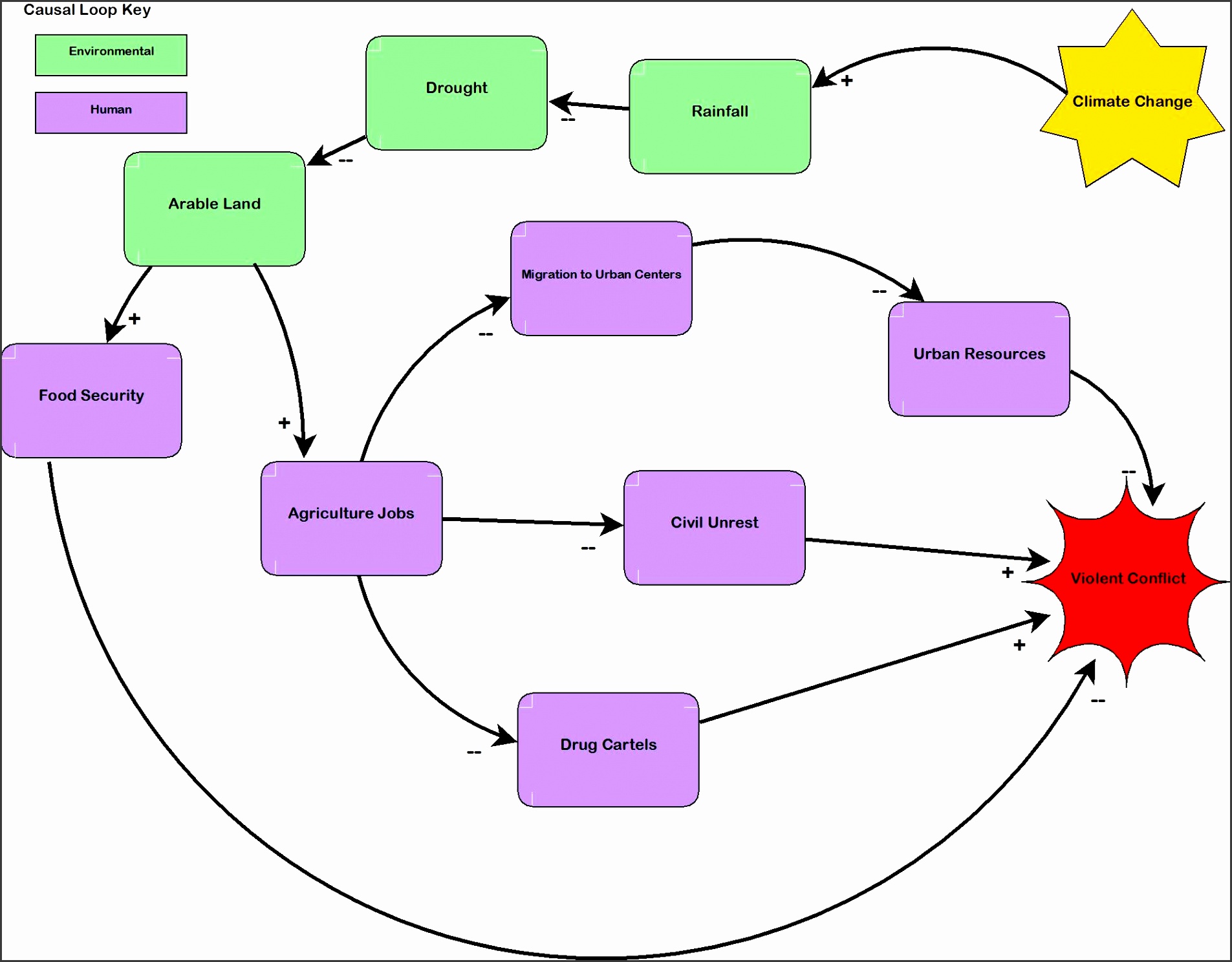
Bubble charts, which are an added dimension of scatter plots, replace the plotted dots with bubbles.
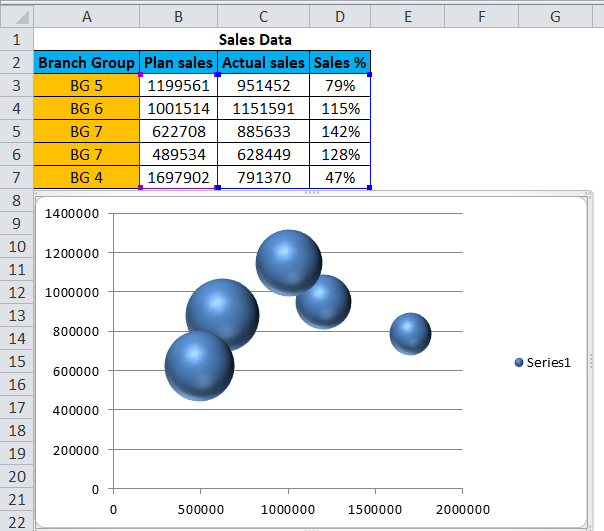
The distribution of the dots across the axes demonstrates the existence, or absence, of correlation between the events. The table below lists the main characteristics of this chart type.In Anaplan, a scatter plot displays values, along two axes, for two sets of data series. Note that this chart type is based upon the XYDiagram, so it can be rotated to change axis positions. Also, you can specify the size of the smallest and largest marker for the chart, by using the BubbleSeriesView.MaxSize and BubbleSeriesView.MinSize properties of the series view.Īn example of the Bubble chart is shown in the image below. You map two dimensions along the usual X and Y axes, and then the third dimension is displayed as a shape (a filled circle - “bubble”, or a star, triangle, etc.) at the data point.
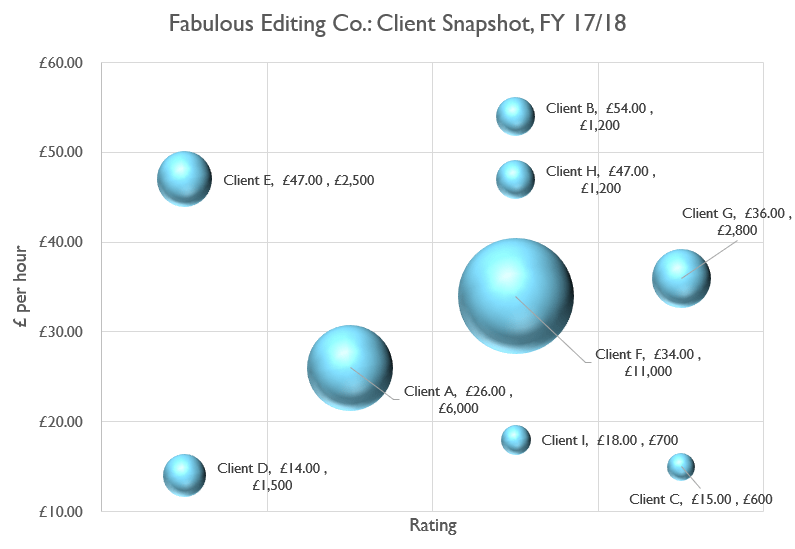
This view, in addition to other point diagram capabilities, allows you to visually represent data that has a third dimension (it is the BubbleLabelValueToDisplay.Weight of a series point), expressed in a bubble’s size. The Bubble Chart is represented by the BubbleSeriesView object, which belongs to Point Series Views.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
